[Android]多语言、Google授权登陆
以此文总结一下《LifeUp》上架 GooglePlay 的全过程~
多语言
App默认会根据系统语言加载不同的字符串资源文件,这是我们实现多语言的基础。
新建资源文件
首先是建立相应的资源文件,可以手动建立,也可以用 Android Studio 的选项建立:
右键 res 文件夹选择File–>New–>Android resource file选择 Locale
可以见到下图
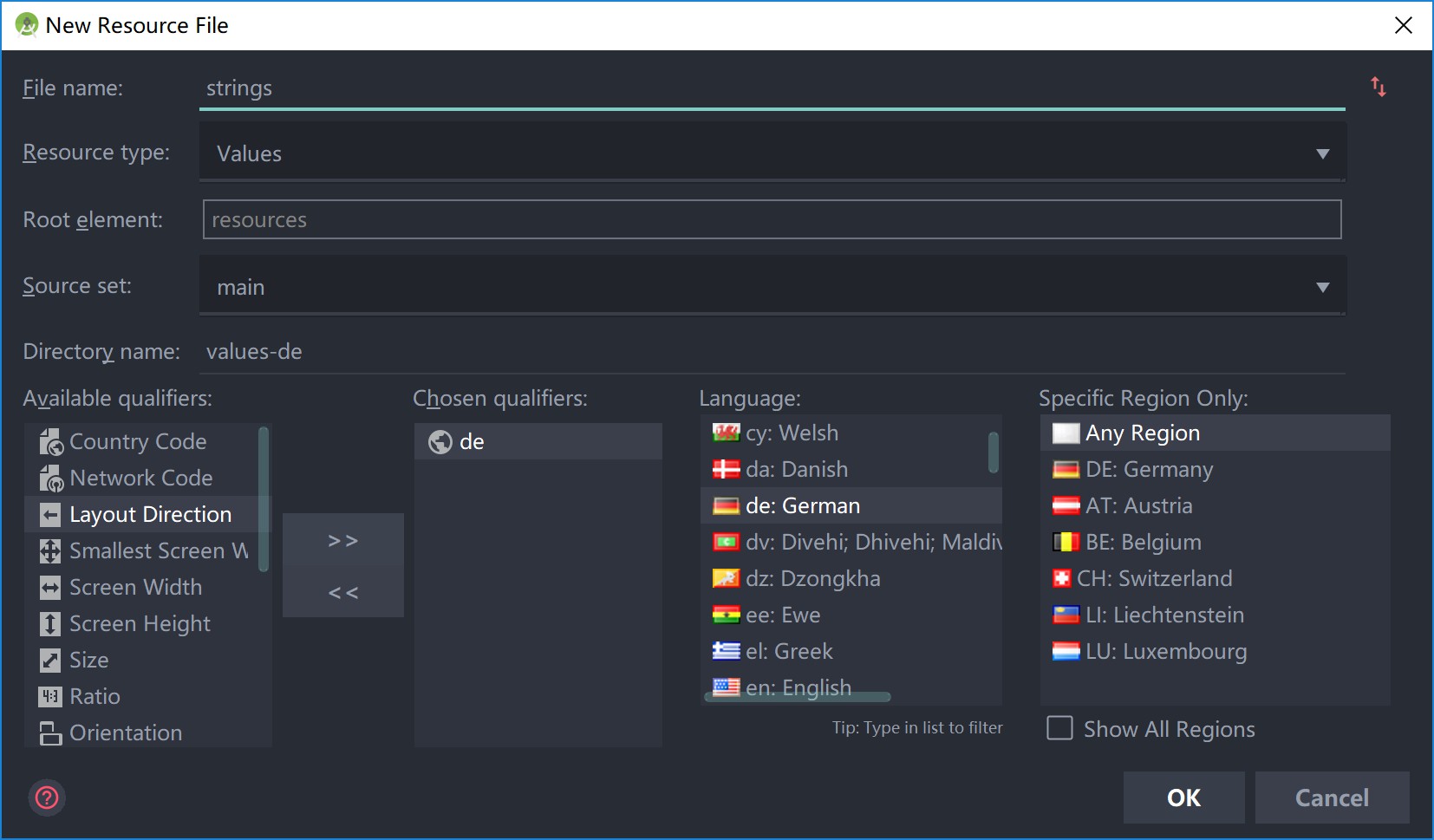
选择你要新建的语言,并且改文件名为strings即可。
实际上,就是新建一个value-(语言缩写)的文件夹(简体中文的话就是value-zh),然后在其中放上string.xml文件。
提取代码、Layout中的字符串
点击相应的字符串,按下ALT+ENTER,然后选择 Extract string resouces。
然后输入字符串资源的名称,勾选相应的资源文件:
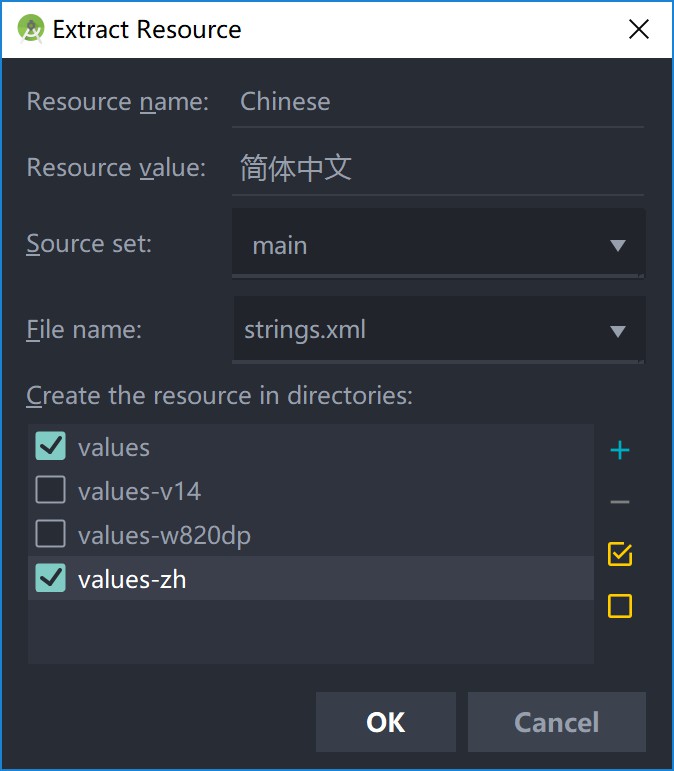
按下确定后,AS就会提取该字符串到资源文件内了,同时代码会被替换成:
Context getString(resouceId)
在Layout中操作同理,利用这个操作可以替换掉App内大部分的静态的字符串。
那么需要动态赋值的字符串该怎么办呢?
字符串资源文件中的变量设置
比如我们的字符串需要传入一个整数型变量的话:
1 | "你已经完成了${getCount()}个任务" // kotlin的String模板写法 |
当然,你可以简单地拆分为两个字符串"你已经完成了"和"个任务",然后
1 | getString(R.string.string1) + getCount() + getString(R.string.string2) |
只是这种写法很不优雅,而且会有些小问题。
getString的时候,会自动去掉取得的字符串头尾的空格,这会让我们不太好控制格式。
特别是英文的时候,经常需要空格隔开。
何况,有些语言我们需要更改语序,这种简单拼接的方法就很不合适。
其实,字符串资源文件里可以用变量占位的方法:
%n$md:代表输出的是整数,n代表是第几个参数,设置m的值可以在输出之前放置空格。
%n$ms:代表输出的是字符串,n代表是第几个参数,设置m的值可以在输出之前放置空格。
%n$mf:代表输出的是浮点数,n代表是第几个参数,设置m的值可以控制小数位数,如m=2.2时,输出格式为0.00。
如果只有一个变量的话,可以直接不写前面的“%n”。
m的值为0的话,也可以留空。
比如上面的例子中,可以在资源文件里这样写:
1 | <string name="task_finish">你已经完成了%1$d个任务,共%2$d个</string> |
英文就可以:
1 | <string name="task_finish">You have already completed %1$d of %2$d tasks</string> |
代码中可以这样传入参数:
1 | // getCompletedCount() 就对应 %1$d,getTotalCount()对应%2$d |
利用这个技巧就能完成整个应用的多语言化了。
多语言切换
主要参考的是上面这篇文章,非常感谢原作者,稍作了一些代码更改。
工具类代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.content.res.Resources;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.LocaleList;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import java.util.Locale;
public class LanguageUtil {
/**
* 中文
*/
public static final Locale LOCALE_CHINESE = Locale.CHINESE;
/**
* 英文
*/
public static final Locale LOCALE_ENGLISH = Locale.ENGLISH;
private static final String LOCALE_SP = "LOCALE_SP";
private static final String LOCALE_SP_KEY = "LOCALE_SP_KEY";
public static Locale getLocale(Context context) {
SharedPreferences spLocale = context.getSharedPreferences(LOCALE_SP, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
String localeJson = spLocale.getString(LOCALE_SP_KEY, "");
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(localeJson))
return null;
Gson gson = new Gson();
return gson.fromJson(localeJson, Locale.class);
}
private static void setLocale(Context pContext, Locale pUserLocale) {
SharedPreferences spLocal = pContext.getSharedPreferences(LOCALE_SP, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor edit = spLocal.edit();
String json = new Gson().toJson(pUserLocale);
edit.putString(LOCALE_SP_KEY, json);
edit.apply();
}
public static void clearLocale(Context pContext) {
SharedPreferences spLocal = pContext.getSharedPreferences(LOCALE_SP, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor edit = spLocal.edit();
edit.putString(LOCALE_SP_KEY, "");
edit.apply();
}
public static boolean updateLocale(Context context, Locale locale) {
if (needUpdateLocale(context, locale)) {
Configuration configuration = context.getResources().getConfiguration();
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1) {
configuration.setLocale(locale);
} else {
configuration.locale = locale;
}
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
context.getResources().updateConfiguration(configuration, displayMetrics);
setLocale(context, locale);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static boolean needUpdateLocale(Context pContext, Locale newUserLocale) {
return newUserLocale != null && !getCurrentLocale(pContext).equals(newUserLocale);
}
public static Locale getCurrentLocale(Context context) {
Locale locale;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) { //7.0有多语言设置获取顶部的语言
locale = context.getResources().getConfiguration().getLocales().get(0);
} else {
locale = context.getResources().getConfiguration().locale;
}
return locale;
}
public static Context languageWork(Context context) {
// 8.0及以上使用createConfigurationContext设置configuration
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
return updateResources(context);
} else {
return context;
}
}
private static Context updateResources(Context context) {
Resources resources = context.getResources();
Locale locale = LanguageUtil.getLocale(context);
if (locale == null) {
return context;
}
Configuration configuration = resources.getConfiguration();
configuration.setLocale(locale);
configuration.setLocales(new LocaleList(locale));
return context.createConfigurationContext(configuration);
}
}BaseActivity配置(Kotlin):
1
2
3
4override fun attachBaseContext(newBase: Context) {
val context = LanguageUtil.languageWork(newBase)
super.attachBaseContext(context)
}工具类使用:
1
LanguageUtil.updateLocale(context, LanguageUtil.LOCALE_ENGLISH)
注意:切换语言后,之前创建的Activity的语言不会马上切换。这里应该引导用户重启应用,或者是想方设法让之前的Activity销毁重建一遍。
接入Google登陆
科学上网肯定是要需要的~这里不提供解决方案。
准备阶段
Google Develper原文:https://developers.google.com/identity/sign-in/android/start-integrating
配置
- Android 设备至少是Android 4.1及以上,并且安装有15.0.0以上版本的 Google Play 服务。
- 项目配置编译版本对应Android 4.1及以上。
- 安装 Google Play Services SDK
- 在Android Studio,选择Tools > Android > SDK Manager。
- 移到底部选择 Extras > Google Repository
Gradle配置
项目级别的build.gradle文件中配置Google的Maven仓库:
1 | allprojects { |
然后在app模块级别的build.gradle文件里,声明Google Play服务依赖:
1 | apply plugin: 'com.android.application' |
配置 Google API 控制台项目
点击原文中的CONFIGURE A PROJECT按钮,然后按照步骤进行就可以配置项目了。
或者前往https://console.developers.google.com/apis/配置也可以。
所需的信息
项目名
签名证书的指纹
可以通过这条命令获取:
1
keytool -exportcert -keystore <将这里替换成你的keystore文件路径,不含尖括号> -list -v
软件包名
获得Client ID
配置完后,你能在Google APIs看到你配置的OAuth 2.0客户端ID。
其中有一个是Web应用类型的,一个是Android应用类型的。
前者是提供给有后端服务器验证需求使用的,具体可以参考:https://developers.google.com/identity/sign-in/android/backend-auth
项目配置实现Google登录
配置 GoogleSignInClient
直接看代码吧:
在activity的
onCreate方法中使用 GoogleSignInOptions 配置你所需要申请的 API 范围:1
2
3
4
5// 配置获取用户ID、邮箱和头像等基础信息
// 其中 DEFAULT_SIGN_IN 用户ID和头像等基础信息。
GoogleSignInOptions gso = new GoogleSignInOptions.Builder(GoogleSignInOptions.DEFAULT_SIGN_IN)
.requestEmail()
.build();同样在
onCreate方法中构建一个 GoogleSIgnInClient 实例1
2// 利用你刚才的gso配置构建GoogleSIgnInClient实例
mGoogleSignInClient = GoogleSignIn.getClient(this, gso);
检查登录状态
1 | // 检查用户是否已经登录过,如果已经登陆过会返回一个GoogleSignInAccount实例 |
布局增加登录按钮
在布局文件中加入:
1
2
3
4<com.google.android.gms.common.SignInButton
android:id="@+id/sign_in_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />你能得到一个这样的登录按钮:

可选:你可以使用setSize方法修改按钮的样式:
1
2
3// 设置登录按钮的尺寸样式
SignInButton signInButton = findViewById(R.id.sign_in_button);
signInButton.setSize(SignInButton.SIZE_STANDARD);设置onClickListener:
1
findViewById(R.id.sign_in_button).setOnClickListener(this);
实现登录逻辑
实现 activity 的onClick方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.sign_in_button:
signIn();
break;
// ...
}
}实现 signIn 方法:
1
2
3
4private void signIn() {
Intent signInIntent = mGoogleSignInClient.getSignInIntent();
startActivityForResult(signInIntent, RC_SIGN_IN);
}在用户登录成功后,你会在activity的
onActivityResult方法回调中获得一个GoogleSignInAccount实例。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
// 结果是从 GoogleSignInClient.getSignInIntent(...) 回调回来的;
if (requestCode == RC_SIGN_IN) {
Task<GoogleSignInAccount> task = GoogleSignIn.getSignedInAccountFromIntent(data);
handleSignInResult(task);
}
}处理GoogleSignInAccount实例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14private void handleSignInResult(Task<GoogleSignInAccount> completedTask) {
try {
GoogleSignInAccount account = completedTask.getResult(ApiException.class);
// 登录成功,更新UI
// 可以通过account.getId()获取Id,account.getDisplayName获得昵称等
updateUI(account);
} catch (ApiException e) {
// ApiException 的状态码代表着错误原因
// 可以参考 GoogleSignInStatusCodes 类查询具体原因
Log.w(TAG, "signInResult:failed code=" + e.getStatusCode());
updateUI(null);
}
}可选:如果你需要让后端去调用相应API,应该通过
1
String idToken = account.getIdToken();
获取到 IdToken 然后通过HTTP POST方法发送给后端,然后后端拿去验证,调用API。
具体参考:https://developers.google.com/identity/sign-in/android/backend-auth
完整登录代码(Kotlin)
1 | class LoginActivity : BaseActivity() { |
[Android]多语言、Google授权登陆